Go SDK
Introduction
To understand how to use this SDK it is best to read the following documentation:
- Server Introduction
First read the Server Introduction to familiarize yourself with the various concepts. - Server API Reference
This Server SDK wraps the Server API and (amongst other things) exposes the responses of the webservice calls as Go objects. Understanding the Server API will help you understanding these SDK objects as well. - This current document will help you understand the global flow when interacting with the Worldline platform using the Go SDK.
The Go SDK helps you to communicate with the Server API. More specifically, it offers a fluent Go API that provides access to all the functionality of the RESTful Server API. Below, we discuss the following topics in detail.
- Initialization of the SDK
- Payments
- File Service support
- Idempotent requests
- Errors
- Logging
- Advanced use: Connection pooling
- Advanced use: Customization of the communication
- Webhooks
- Notes
The source code of the SDK is available on Github . There you can find installation instructions.
The API documentation of the latest version of the SDK is available here . Note that this is only available for versions 3.x and later. For version 2.x use this URL instead.
Initialization of the Go SDK
All Go code snippets presented in the API reference assume you have initialized the Go SDK before using them in your Development Environment. This section details the initialization of the Go SDK.
Initializing is simple, and requires only one key task: use our connectsdk.CreateClient function to create a connectsdk.Client instance, which contains the actual methods to communicate with the Server API.
The connectsdk.CreateClient function needs the following input information to provide you with an initialized connectsdk.Client
- The secretAPIKey and apiKeyID. The secretAPIKey is a key that is used to authenticate your API requests, and apiKeyID identifies that key (as you can have multiple active keys). Both of these can be obtained from the Account Setup tab of the Configuration Center, and are available only if you are administrator.
- The name of the integrator, e.g. your company name
You can create an instance of connectsdk.Client using the connectsdk.CreateClient function with this code snippet:
client, _ := connectsdk.CreateClient("apiKeyID", "secretAPIKey", "integrator")This connectsdk.Client instance offers connection pooling and can be reused for multiple concurrent API calls. Once it is no longer used it should be closed.
The client can be closed after usage by calling the following code right after the client is created:
defer client.Close()Using CommunicatorConfiguration
You can specify more options by using a configuration.CommunicatorConfiguration object. You can configure extra properties on this object as needed. For example, using an in-memory TOML file:
conf, _ := connectsdk.CreateV1HMACConfiguration("apiKeyID", "secretAPIKey", "integrator")
tomlData := `
ConnectTimeout = 5000000000
SocketTimeout = 300000000000
MaxConnections = 10
AuthorizationType = "v1HMAC"
[APIEndpoint]
host = "api.domain.com"
`
toml.Decode(tomlData, conf)
client, _ := connectsdk.CreateClientFromConfiguration(conf)These values are the default values. We recommend to keep the timeout values at these values. See API endpoints for the possible hosts.
If a proxy should be used, the configuration.CommunicatorConfiguration object should have one extra property set, Proxy *url.URL . If the proxy requires authentication, then this should be set as the Userinfo of the URL.
The timeouts are defined as time.Duration properties. When using TOML, these only support the default time unit, which is nanoseconds. To convert a number of seconds to nanoseconds, add 9 zeroes. For instance, the ConnectTimeout value above is 5 seconds, and the SocketTimeout value is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Client meta information
Optionally, for BI and fraud prevention purposes, you can supply meta information about the client used by the customer. To do so, create a new instance of connectsdk.Client at the start of the customer's payment process as follows:
consumerSpecificClient := client.WithClientMetaInfo("consumer specific JSON meta info")This consumer specific instance will use the same connection pool as the connectsdk.Client from which it was created. As a result, closing a connectsdk.Client will close all connectsdk.Client instances created using the WithClientMetaInfo method. There is no need to close those separately.
This closing works both ways. If a connectsdk.Client created using the WithClientMetaInfo method is closed this will also close the connectsdk.Client it originated from. This will in turn close all other connectsdk.Client instances created using the WithClientMetaInfo method. This can be used if only a connectsdk.Client with client meta info is needed.
Do not use this consumer specific instance for API calls for other consumers.
Example JSON meta information for a mobile app client:
X-GCS-ClientMetaInfo: {
"platformIdentifier": "Android/4.4",
"appIdentifier": "Example mobile app/1.1",
"sdkIdentifier": "AndroidClientSDK/v1.2",
"screenSize": "800x600",
"deviceBrand": "Samsung",
"deviceType": "GT9300",
"ipAddress": "123.123.123.123"
}Example JSON meta information for the JavaScript SDK running in a browser:
X-GCS-ClientMetaInfo: {
"platformIdentifier": "Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; U; Android 4.1.1; en-gb; Build/KLP) AppleWebKit/534.30 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/534.30",
"sdkIdentifier": "JavaScriptClientSDK/v1.2",
"screenSize": "800x600"
}Payments
As a merchant, your core interaction with Worldline typically starts when your customer clicks the checkout button in your application. The payment process usually has the following steps:
- Payment Product selection
- Setting of available information needed for selected payment product (e.g. amount of the order)
- Collection of missing customer information needed for selected payment product (e.g. creditcard number)
- Submitting the payment request to the Worldline platform
- Handling the response to the payment request (e.g. payment unsuccessful)
The Worldline platform offers three ways of handling this payment process:
- Use a hosted payment through the MyCheckout hosted payment pages.
In this case, you redirect the customer to our hosted payment pages. For you as a merchant, this is the easiest option as the Worldline platform can handle payment product selection and is responsible for the collection of sensitive data like a creditcard number. Through our Configuration Center, you still have a lot of control over the look and feel of the checkout. - Use a Client SDK to build a payment flow for a native app or a JavaScript application.
In this case, your server requests the creation of a client session. This returns a session id with which your client application can communicate with the Worldline platform directly. Your client collects and then encrypts the required customer information. It then sends this encrypted information to your server, where you add all other relevant information and submit a payment request to the Worldline platform. - Use a Server SDK to build a payment flow hosted on your server.
In this case, you can use the Server SDK to obtain the payment products that are applicable to the payment, to obtain the fields that need to be collected from the customer for a selected payment product, and to submit the payment request itself.
In the next couple of paragraphs, we discuss each of these options in more detail.
Use a hosted payment through the MyCheckout hosted payment pages
The high-level flow of a hosted payment is described below, followed by a more detailed look at each of the steps. 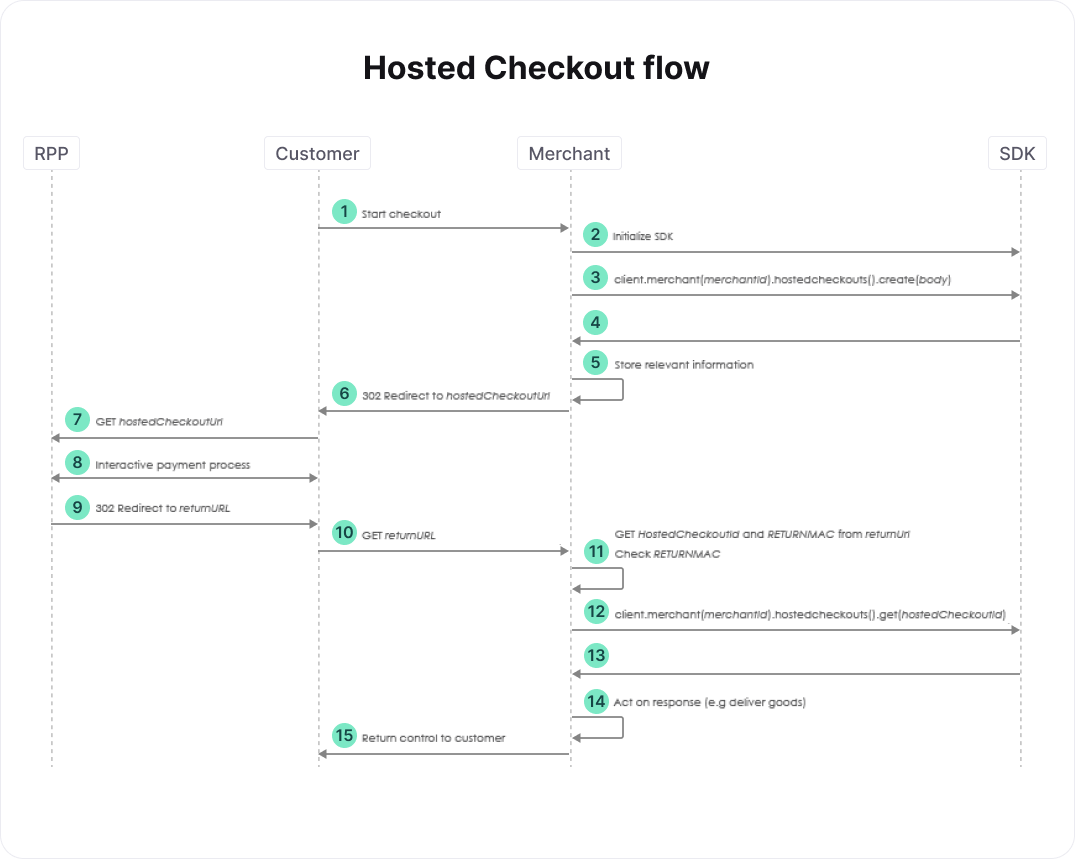
- At this point, your customer has provided all relevant information regarding the order, e.g. a shopping cart of items and a shipping address.
- See the section on initialization. Use the connectsdk.CreateClient or connectsdk.CreateClientFromConfiguration function to create an instance of connectsdk.Client if you hadn't done so yet, and set the metadata that you've collected about the client of the customer.
- Create a domain.CreateHostedCheckoutRequest body and populate at least its Order. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. You can specify an optional ReturnURL, which is used to redirect your customer back to your website in step 9.
- The create hosted checkout SDK call returns a domain.CreateHostedCheckoutResponse response. Store the HostedCheckoutID and RETURNMAC it contains, as well as any other relevant order information. You will need these when your customer returns from our hosted payment pages, or when the customer fails to return in a reasonable amount of time. Now take response.PartialRedirectURL and prepend "https://yoursubdomain" to it to create HostedCheckoutURL, where yoursubdomain is a subdomain of the MyCheckout hosted payment pages you requested. You can find your subdomains in the Configuration Center's Payment Page Setup tab, under the Subdomain settings of your merchant. If you are logged in as an adminstrator, you can request a subdomain here as well.
- After completing the interactive payment process in the MyCheckout hosted payment pages, your customer is redirected back to the url you provided in step 3 as body.HostedCheckoutSpecificInput.ReturnURL. The HostedCheckoutID and RETURNMAC you stored in step 5 are added to this URL as query parameters. Specifying a ReturnURL is optional, however. As a result, your customer is only redirected back if you've provided a URL in step 3.
- If you cannot identify the customer based on e.g. the HTTP session, you can use the HostedCheckoutID for this purpose. If you do, you must check that the HostedCheckoutID and RETURNMAC from the ReturnURL match those that you stored in step 3. Note that the RETURNMAC is used as a shared secret between the Worldline platform and your system that is specific for this hosted checkout.
- Retrieve the results of the customer's interaction with the Worldline platform.
- Check the domain.GetHostedCheckoutResponse response returned in step 13. If response.Status equals PAYMENT_CREATED, then the customer attempted a payment, the details of which can be found in response.CreatedPaymentOutput. Depending on the payment product chosen and the status of the payment you can "deliver the goods" immediately, or set up a regular poll of the created payment to wait for the status. Such a poll is done using the SDK call client.V1().Merchant("merchantID").Payments().Get(paymentID, nil), where paymentID is response.CreatedPaymentOutput.Payment.ID. For details on the various payment products and their statuses, see Payment Products.
Additionally, it may be the case that the customer does not return in time (or at all), for example because the browser is closed or because you didn't provide a ReturnURL. In this case, you need to retrieve the status of the hosted checkout (step 12) before the hosted checkout times out, which happens after 2 hours, and follow step 14 as well.
Use a Client SDK to build a payment flow for a native app or a JavaScript application
The high-level flow of a payment performed with a native app or a JavaScript application is described below, followed by a more detailed look at each of the steps. First, we discuss the flow for payment products that do not require a redirect to a payment method hosted by a third party. Afterwards, the flow for payment methods that require a redirect is described.
Although this flow uses the Client SDK, we won't go into the details of this SDK here. A detailed description is given in the documentation of the Client SDK. 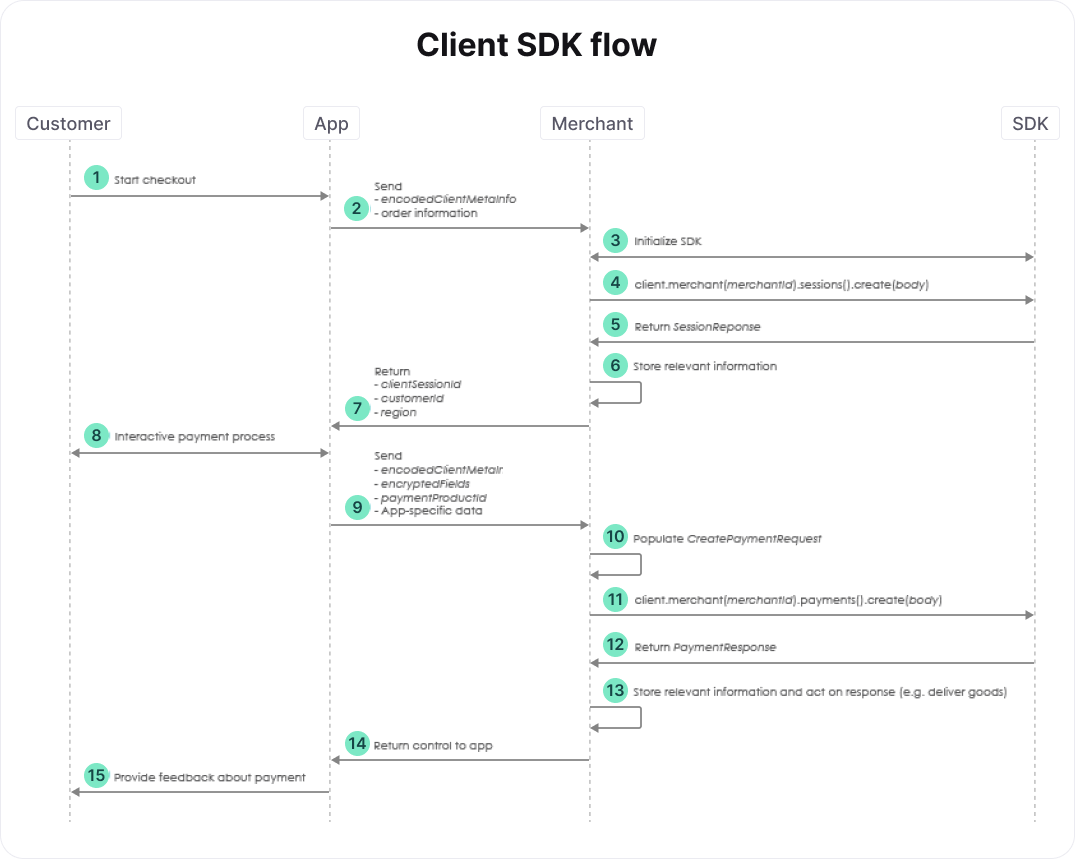
- At this point, your customer has provided all relevant information regarding the order, e.g. a shopping cart of items and a shipping address.
- The app sends the metadata about the client of the customer and the order information to your server.
- See the section on initialization. Use the connectsdk.CreateClient or connectsdk.CreateClientFromConfiguration function to create an instance of connectsdk.Client if you hadn't done so yet, and set the metadata about the client of the customer provided in the previous step.
- Create a domain.SessionRequest body and request a new session. By creating a session, you allow your consumer to communicate with our Client API via your app. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. Requesting a new session results in a domain.SessionResponse response, which contains a ClientSessionID, CustomerID, and a Region. Store the relevant information to be able to link the order and customer to the payment.
- Send the ClientSessionID, CustomerID, and Region to the app. The Client SDK needs this information to interact with the Client API. As mentioned above, the documentation of the Client SDK provides additional details.
- Once the interactive payment process is finished, the app has to send the encodedClientMetaInfo, encryptedFields, and paymentProductId to your server. The encryptedFields contains confidential information about the payment request. Do not store it anywhere. Use the paymentProductId to determine which additional fields you need to provide in the payment request. Some of these fields may come from your app, so you can decide to send additional app-specific data to your server. For payments that require a redirect to a third party, for example, you could send a return URL as app-specific data. Note that for this flow, we assume that we're dealing with a payment that doesn't require a redirect.
- Create a domain.CreatePaymentRequest body. Populate its EncryptedCustomerInput with the encryptedFields obtained from the app. Also populate its Order. You may also want to populate the FraudFields and the relevant PaymentMethodSpecificInput. To this end, you can map the paymentProductId obtained from the app to its payment method. For example, for a card payment, you can populate CardPaymentMethodSpecificInput to e.g. set a CustomerReference or indicate that the payment is the first of a recurring sequence.
- Use the body you just created to perform a create payment request. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. The create payment SDK call returns a domain.CreatePaymentResponse response. The status of the payment is accessible via response.Payment.Status. Depending on the payment product chosen and the status of the payment you can "deliver the goods" immediately, or set up a regular poll of the created payment to wait for the status. Such a poll is done using the SDK call client.V1().Merchant("merchantID").Payments().Get(paymentID, nil), where paymentID is response.Payment.ID. For details on the various payment products and their statuses, see Payment Products.
The high-level flow of a payment performed with a native app or a JavaScript application is a little different if a redirect is involved. We only describe the steps that differ from the flow without a redirect. 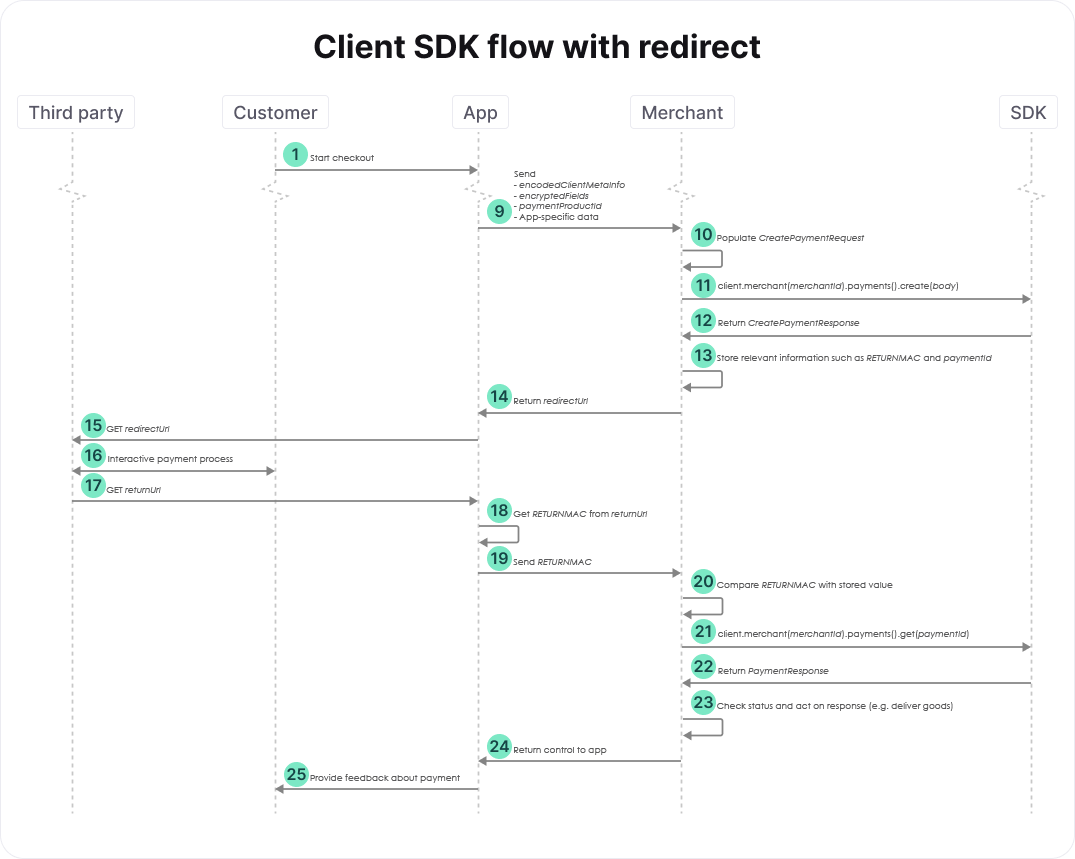
- The payment process shown in the diagram above involves a redirect of your customer. For this example, we assume that the app decides which ReturnURL should be used, which is sent as part of the app-specific data. Your customer is redirected to this URL (i.e., is send back to your app) after completing the payment process. The paymentProductId can be used to determine whether we're dealing with a payment that involves a redirect.
- Create a domain.CreatePaymentRequest body and populate its EncryptedCustomerInput and its Order. Additionally, populate its RedirectPaymentMethodSpecificInput by providing at least the desired ReturnURL. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details.
- The create payment SDK call returns a domain.CreatePaymentResponse response. For payments involving a redirect, response.MerchantAction.RedirectData.RedirectURL defines the URL to which the customer should be redirected to complete the payment. You need to store the value ofresponse.MerchantAction.RedirectData.RETURNMAC because it should be compared with theRETURNMAC returned by the app at a later stage. Additionally, you need to store the value ofresponse.Payment.ID. This paymentID is needed to check the status of the payment after the redirect.
- Send the RedirectURL to your app so that it can redirect the customer to the payment page hosted by the third party.
- After the payment process is completed, your customer is redirected to the ReturnURL specified previously. In the flow shown in the figure above, we assume that this URL brings the customer back to the app.
- The app should retrieve the RETURNMAC from the returnUrl and send it to your server.
- You can use the RETURNMAC to identify the customer by comparing it with the one stored previously, and to validate that the customer was redirected to you by our systems.
- Use the paymentID stored previously to check the status of the payment. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. The retrieve payment SDK call returns a domain.PaymentResponse response. The status of the payment is accessible via response.Payment.Status. Use this status to handle the order appropriately, as described above.
Use a Server SDK to build a payment flow hosted on your server
The high-level flow of a payment performed from pages hosted on your server is described below, followed by a more detailed look at each of the steps. First, we describe the flow for payment products that do not require a redirect to a payment method hosted by a third party. Afterwards, the flow for payment methods that require a redirect is described. 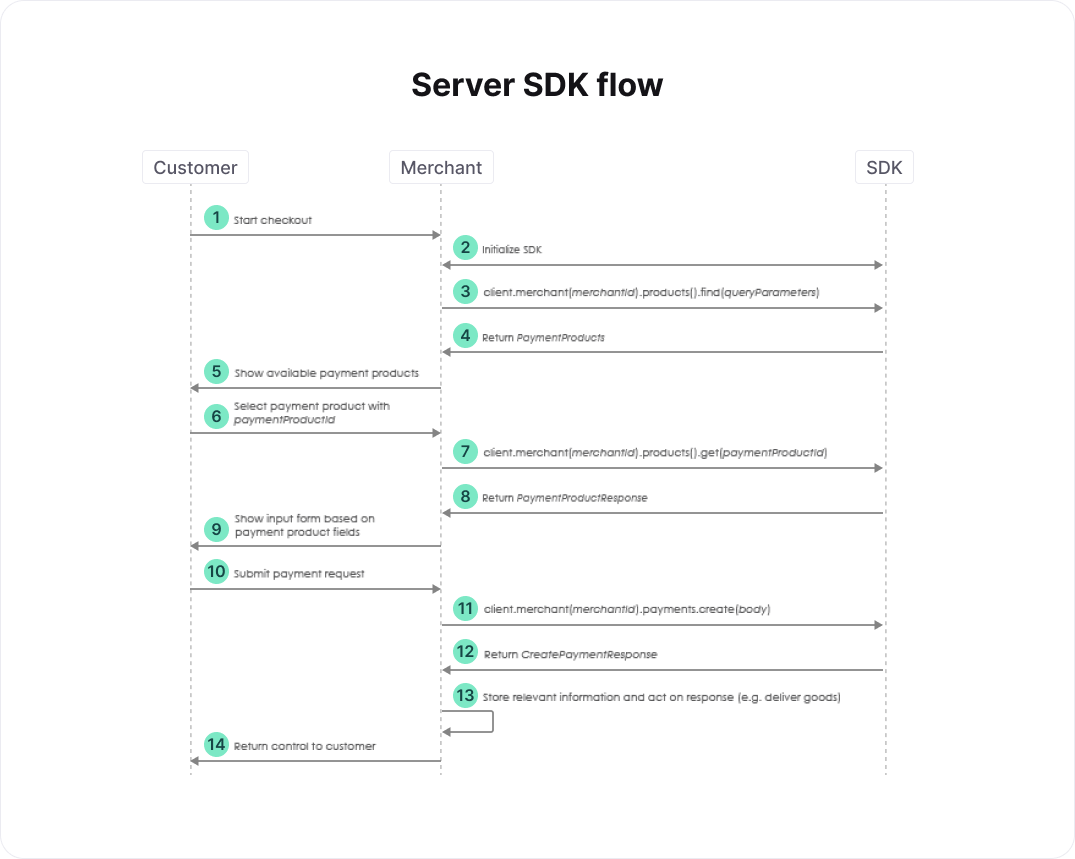
- At this point, your customer has provided all relevant information regarding the order, e.g. a shopping cart of items and a shipping address.
- See the section on initialization. Use the connectsdk.CreateClient or connectsdk.CreateClientFromConfiguration function to create an instance of connectsdk.Client if you hadn't done so yet, and set the metadata that you've collected about the client of the customer.
- Create products.FindParams queryParams and request a list of relevant payment products. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details.
- Show the relevant payment products to the customer such that he or she can select one.
- The customer selects one of available the payment products.
- Once the customer has decided which payment product should be used, you request the fields of this payment product. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details.
- Based on the information retrieved in the previous step, you render a form that the customer can use to enter all relevant information for the selected payment product.
- The customer submits the form.
- Create a domain.CreatePaymentRequest body, populate its Order and other properties depending on the selected payment product, and submit it. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. Do not store the information provided by the customer. The paymentProductId can be used to determine whether this payment involves a redirect to a third party. For this flow, we assume that we're dealing with a payment that doesn't require a redirect.
- The create payment SDK call returns a domain.CreatePaymentResponse response. The status of the payment is accessible via response.Payment.Status. Depending on the payment product chosen and the status of the payment you can "deliver the goods" immediately, or set up a regular poll of the created payment to wait for the status. Such a poll is done using the SDK call client.V1().Merchant("merchantID").Payments().Get(paymentID, nil), where paymentID is response.Payment.Id. For details on the various payment products and their statuses, see Payment Products.
The high-level flow of a payment performed from pages on your server is a little different if a redirect is involved. We only describe the steps that differ from the flow without a redirect. 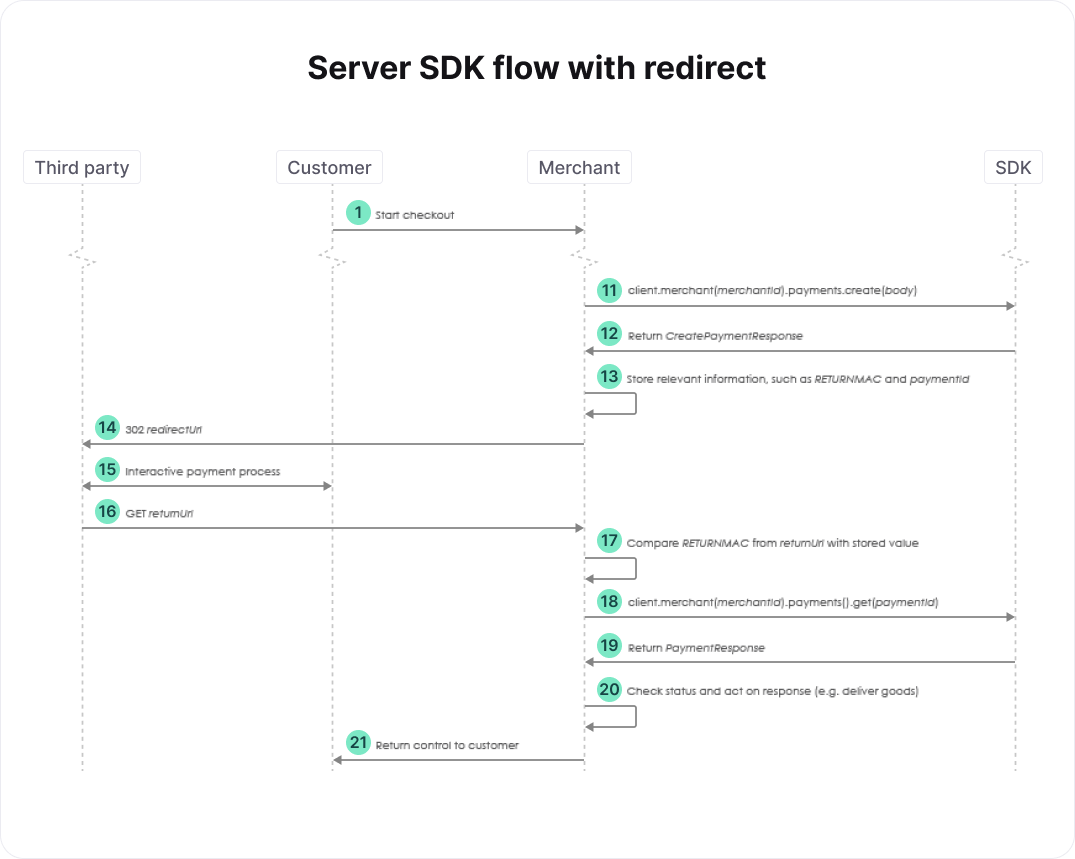
- We assume that we're dealing with a payment that involves a redirect. As mentioned above, this can be determined using the paymentProductId. Create a domain.CreatePaymentRequest body and populate at least its Order. Additionally, populate its RedirectPaymentMethodSpecificInput by providing at least the desired ReturnURL. The ReturnURL defines the location to which the customer should be redirected after completing the payment process. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details.
- The create payment SDK call returns a domain.CreatePaymentResponse response. For payments involving a redirect, response.MerchantAction.RedirectData.RedirectURL defines the URL to which the customer should be redirected to complete the payment. You need to store the value ofresponse.MerchantAction.RedirectData.RETURNMAC because it should be compared with theRETURNMAC returned by the third party at a later stage. Additionally, you need to store the value ofresponse.Payment.ID. This paymentID is needed to check the status of the payment after the redirect.
- Redirect the customer to the redirectUrl.
- After the payment process is completed, your customer is redirected to the ReturnURL specified previously. In the flow shown in the figure above, we assume that this URL brings the customer back to your server.
- Retrieve the RETURNMAC provided by the third party from the returnUrl. You can use the RETURNMAC to identify the customer by comparing it with the one stored previously, and to validate that the customer was redirected to you by our systems.
- Use the paymentID stored previously to check the status of the payment. See the relevant section of the full API reference for more details. The retrieve payment SDK call returns a domain.PaymentResponse response. The status of the payment is accessible via response.Payment.Status. Use this status to handle the order appropriately, as described above.
File Service support
Uploading files
To upload a file, you need to create an instance of struct domain.UploadableFile as part of your request. This struct encapsulates the following properties:
- The name of the file (without any path).
- The content of the file, as an io.Reader. Its source could be a file on disk, a database record, or even a string.
If this io.Reader is also an io.ReadCloser, you must make sure it is closed after the upload call has finished, preferably using a deferred call to Close(). The SDK will not close it for you.
- The content type, e.g. application/pdf. Please check the API references for the allowed formats. You can find an incomplete list of content types (also called MIME types) here .
- Optionally, the content length (the size of the file).
Downloading files
To download a file, you need to provide a function of type communicator.BodyHandler. This function takes the following arguments and can return an error:
- A list of response headers. These should include at least the Content-Type and Content-Disposition headers. Functions communication.GetHeaderValue and communication.GetDispositionFilename can be called on the headers list to extract the content type and the name of the downloaded file.
- The content of the file, as an io.Reader. You can copy its contents to any destination you like, e.g. a file on disk or a database record..
This io.Reader is managed by the SDK, and will be closed after the function finishes. You should not close it yourself.
Idempotent requests
To execute a request as an idempotent request, you can call the same method as for a non-idempotent request, but with an extra communicator.CallContext argument with its IdempotenceKey property set. This will make sure the SDK will send an X-GCS-Idempotence-Key header with the idempotence key as its value.
If a subsequent request is sent with the same idempotence key, the response will contain an X-GCS-Idempotence-Request-Timestamp header, and the SDK will set the IdempotenceRequestTimestamp property of the communicator.CallContext argument. If the first request has not finished yet, the RESTful Server API will return a 409 status code. If this occurs, the SDK will return an errors.IdempotenceError with the original idempotence key and the idempotence request timestamp.
For example:
context := connectsdk.NewCallContext(idempotenceKey)
response, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Create(request, context)
if e, ok := err.(*errors.IdempotenceError); ok {
// a request with the same idempotenceKey is still in progress, try again after a short pause
// e.IdempotenceRequestTimestamp() contains the value of the
// X-GCS-Idempotence-Request-Timestamp header
}
idempotenceRequestTimestamp := context.GetIdempotenceRequestTimestamp()
// idempotenceRequestTimestamp contains the value of the
// X-GCS-Idempotence-Request-Timestamp header
// if idempotenceRequestTimestamp is not null this was not the first requestErrors
Payment errors
If a payment attempt is declined by the RESTful Server API, an errors.DeclinedPaymentError is returned. This error contains a reference to the payment result which can be inspected to find the reason why the payment attempt was declined. This payment result can also be used to later retrieve the payment attempt again.
For example:
response, error := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Create(request, nil)
if e, ok := err.(*errors.DeclinedPaymentError); ok {
payment := e.PaymentResult().Payment
paymentID := payment.ID
paymentStatus := payment.Status
if paymentStatus == nil {
fmt.Println("Payment", *paymentId, "was declined with an unknown status")
} else {
fmt.Println("Payment", *paymentId, "was declined with status", *paymentStatus)
}
}Unlike direct payments, indirect payments like iDeal and PayPal usually will not cause an errors.DeclinedPaymentError to be returned, but instead will result in a domain.CreatePaymentResponse return value. To determine if the payment was successfully finished, declined or cancelled, you would need to retrieve the payment status and examine its contents, especially the status field. It is recommended to use shared code for handling errors.
For example:
var paymentID *string
response, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Create(request, nil)
if e, ok := err.(*errors.DeclinedPaymentError); ok {
payment := e.PaymentResult().Payment
handlePaymentError(payment)
return
}
if err == nil {
paymentID = response.Payment.ID
// other code
payment, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Get(*paymentID)
if isNotSuccessful(payment) {
handlePaymentError(payment)
}
}Payout errors
If a payout attempt is declined by the RESTful Server API, an errors.DeclinedPayoutError is returned. This error contains a reference to the payout result which can be inspected to find the reason why the payout attempt was declined. This payout result can also be used to later retrieve the payout attempt again.
For example:
response, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payouts().Create(request)
if e, ok := err.(*errors.DeclinedPayoutError); ok {
payout := e.PayoutResult()
payoutID := payout.ID
payoutStatus := payout.Status
if payoutStatus == nil {
fmt.Println("Payout", *payoutID, "was declined with an unknown status")
} else {
fmt.Println("Payout", *payoutID, "was declined with status", *payoutStatus)
}
}Refund errors
If a refund attempt is declined by the RESTful Server API, an errors.DeclinedRefundError is returned. This error contains a reference to the refund result which can be inspected to find the reason why the refund was declined. This refund result can also be used to later retrieve the refund attempt again.
For example:
response, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Refund(paymentID, request, nil)
if e, ok := err.(*errors.DeclinedRefundError); ok {
refund := e.RefundResult()
refundID := refund.ID
refundStatus := refund.Status
if refundStatus == nil {
fmt.Println("Refund", *refundID, "was declined with an unknown status")
} else {
fmt.Println("Refund", *refundID, "was declined with status", *refundStatus)
}
}Other errors
Besides the above errors, all calls can return one of the following errors:
- An errors.ValidationError if the request was not correct and couldn't be processed (HTTP status code 400)
- An errors.AuthorizationError if the request was not allowed (HTTP status code 403)
- An errors.IdempotenceError if an idempotent request caused a conflict (HTTP status code 409)
- An errors.ReferenceError if an object was attempted to be referenced that doesn't exist or has been removed, or there was a conflict (HTTP status code 404, 409 or 410)
- An errors.PlatformError if something went wrong on the Worldline platform. The Worldline platform was unable to process a message from a downstream partner/acquirer, or the service that you're trying to reach is temporary unavailable (HTTP status code 500, 502 or 503)
- An errors.APIError if the RESTful Server API returned any other error
A payment attempt can now be handled as follows:
response, err := client.V1().Merchants(merchantID).Payments().Create(request, nil)
switch e := err.(type)
case *errors.DeclinedPaymentError:
payment := e.PaymentResult().Payment
paymentID := payment.ID
paymentStatus := payment.Status
if paymentStatus == nil {
fmt.Println("Payment", *paymentID, "was declined with an unknown status")
} else {
fmt.Println("Payment", *paymentID, "was declined with status", *paymentStatus)
}
case *errors.ValidationError:
fmt.Println("Input validation error:")
for (_, apiErr := range e.Errors()) {
if apiErr.PropertyName == nil) {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
} else {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.PropertyName, ":",
*apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
}
}
case *errors.AuthorizationError:
fmt.Println("Authorization error:")
for (_, apiErr := range e.Errors()) {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
}
case *errors.ReferenceError:
fmt.Println("Incorrect object reference:")
for (_, apiErr := range e.Errors()) {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
}
case *errors.PlatformError:
fmt.Println("Error occurred at Worldline or a downstream partner/acquirer:")
for (_, apiErr := range e.Errors()) {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
}
case errors.APIError:
fmt.Println("Worldline error:")
for (_, apiErr := range e.Errors()) {
fmt.Println("-", *apiErr.Code, ":", *apiErr.Message)
}
default:
// An internal errorError overview
The following table is a summary that shows when each of these errors will be returned:
| HTTP status code | Meaning | Description | Error Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | Successful | Your request was processed correctly | N/A |
| 201 | Created | Your request was processed correctly and a new resource was created. The URI of this created resource is returned in the Location header of the response. |
N/A |
| 204 | No Content | Your request was processed correctly | N/A |
| various; domain.CreatePaymentResult is present in the response | Payment Rejected | Your request was rejected either by the Worldline platform or one of our downstream partners/acquirers. | errors.DeclinedPaymentError |
| various; domain.PayoutResult is present in the response | Payout Rejected | Your request was rejected either by the Worldline platform or one of our downstream partners/acquirers. | errors.DeclinedPayoutError |
| various; domain.RefundResult is present in the response | Refund Rejected | Your request was rejected either by the Worldline platform or one of our downstream partners/acquirers. | errors.DeclinedRefundError |
| 400 | Bad Request | Your request is not correct and can't be processed. Please correct the mistake and try again. | errors.ValidationError |
| 403 | Not Authorized | You're trying to do something that is not allowed or that you're not authorized to do. | errors.AuthorizationError |
| 404 | Not Found | The object you were trying to access could not be found on the server. | errors.ReferenceError |
| 409 | Conflict | Your idempotent request resulted in a conflict. The first request has not finished yet. | errors.IdempotenceError |
| 409 | Conflict | Your request resulted in a conflict. Either you submitted a duplicate request or you're trying to create something with a duplicate key. | errors.ReferenceError |
| 410 | Gone | The object that you are trying to reach has been removed. | errors.ReferenceError |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | Something went wrong on the Worldline platform. | errors.PlatformError |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | The Worldline platform was unable to process a message from a downstream partner/acquirer. | errors.PlatformError |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | The service that you're trying to reach is temporary unavailable. Please try again later. |
errors.PlatformError |
| other | Unexpected error | An unexpected error has occurred | errors.APIError |
Logging
The Go SDK supports logging of requests, responses and errors of the API communication.
In order to start using the logging feature, an implementation of the logging.CommunicatorLogger interface should be provided. The SDK provides two example implementations for logging to os.Stdout (logging.StdOutCommunicatorLogger) and logging to a standard Go logger (logging.DefaultLogCommunicatorLogger).
Logging can be enabled by calling the EnableLogging method on a connectsdk.Client object, and providing the logger as an argument. The logger can subsequently be disabled by calling the DisableLogging method.
When logged messages contain sensitive data, this data is obfuscated.
The following code exemplifies the use of adding a logger:
client, _ := connectsdk.CreateClient("apiKeyID", "secretAPIKey", "integrator")
logger, _ := logging.NewDefaultLogCommunicatorLogger(log.Logger{})
client.EnableLogging(logger)
//... Do some calls
client.DisableLogging()Advanced use: Connection pooling
A connectsdk.Client created using the connectsdk.CreateClient or connectsdk.CreateClientFromConfiguration function will use its own connection pool. If multiple clients should share a single connection pool, the connectsdk.CreateCommunicator or connectsdk.CreateCommunicatorFromConfiguration function should be used to first create a shared communicator.Communicator, then the connectsdk.CreateClientFromCommunicator function should be used to create connectsdk.Client instances that use that communicator.Communicator:
communicator, _ := connectsdk.CreateCommunicator("apiKeyID", "secretAPIKey", "integrator")
// create one or more clients using the shared communicator
client, _ := connectsdk.CreateClientFromCommunicator(communicator)Instead of closing these connectsdk.Client instances, you should instead close the communicator.Communicator when it is no longer needed. This will close all connectsdk.Client instances that use the communicator.Communicator.
If instead one of the connectsdk.Client instances is closed, the communicator.Communicator will be closed as well. As a result, all other connectsdk.Client instances that use the communicator.Communicator will also be closed. Attempting to use a closed connectsdk.Client or communicator.Communicator will result in an error.
Just like connectsdk.Client, communicator.Communicator instances can be closed after usage by calling the following code right after the communicator is created:
defer communicator.Close()Connection management
Just like connectsdk.Client, communicator.Communicator also has method CloseExpiredConnections that can be used to evict expired HTTP connections. You can call this method on the communicator.Communicator instead of on any of the connectsdk.Client instances. The effect will be the same.
Advanced use: Customization of the communication
A connectsdk.Client uses a communicator.Communicator to communicate with the RESTful Server API. A communicator.Communicator contains all the logic to transform a request object to a HTTP request and a HTTP response to a response object. The functionality of the communicator.Communicator is built on the following:
- The RESTful Server API endpoint URI.
- A communicator.Connection, which represents one or more HTTP connections to the Worldline server.
- An authentication.Authenticator, which is used to sign your requests.
- A communicator.MetadataProvider, which constructs the header with metadata of your server that is sent in requests for BI and fraud prevention purposes.
- A json.Marshaller, which is used to marshal and unmarshal request and response objects to and from JSON.
For your convenience, a connectsdk.CommunicatorBuilder is provided to easily replace one or more of these components. For example, to instantiate a connectsdk.Client that uses your own implementation of communicator.Connection, you can use the following code snippet:
connection := YourConnection{}
communicatorBuilder, _ := connectsdk.CreateCommunicatorBuilder("apiKeyID", "secretAPIKey", "integrator")
communicator, _ := communicatorBuilder.WithConnection(connection).Build()
client, _ := connectsdk.CreateClientFromCommunicator(communicator)Logging
To facilitate implementing logging in a custom communicator.Connection, the SDK provides utility structs logging.RequestLogMessageBuilder and logging.ResponseLogMessageBuilder. These can be used to easily construct request and response messages. For instance:
// In the below code, logger is the logging.CommunicatorLogger set using EnableLogging.
// Note that it may be null if EnableLogging is not called.
requestID := createRequestID() // Create a unique id; function to be provided by you
requestLogMessageBuilder, _ := NewRequestLogMessageBuilder(requestID, method, uri,
obfuscation.DefaultBodyObfuscator(), obfuscation.DefaultHeaderObfuscator()
)
// add request headers to requestLogMessageBuilder
// if present, set the request body on requestLogMessageBuilder
logger.LogRequestLogMessage(requestLogMessageBuilder.BuildMessage().String())
start := time.Now()
// send the request
end := time.Now()
duration := end.Sub(start)
statusCode := ...
responseLogMessageBuilder, _ := NewResponseLogMessageBuilder(requestID, statusCode, duration,
obfuscation.DefaultBodyObfuscator(), obfuscation.DefaultHeaderObfuscator())
// add response headers to responseLogMessageBuilder
// if present, set the response body on responseLogMessageBuilder
logger.LogResponseLogMessage(responseLogMessageBuilder.BuildMessage().String())Webhooks
The part of the SDK that handles the webhooks support is called the webhooks helper. It transparently handles both validation of signatures against the event bodies sent by the webhooks system (including finding the secret key for key ids), and unmarshalling of these bodies to objects. This allows you to focus on the essentials, and not the additional overhead.
Providing secret keys
Secret keys are provided to the webhooks helper using implementations of interface validation.SecretKeyStore. The Go SDK provides one implementation, which is returned by function webhooks.InMemorySecretKeyStore. This will use secret keys that are stored in-memory and managed through functions webhooks.StoreInMemorySecretKey, webhooks.RemoveInMemorySecretKey and webhooks.ClearInMemorySecretKeys. If more advanced storage is required, e.g. using a database or file system, then you should write your own implementation.
Initialization of the webhooks helper
Using an implementation of validation.SecretKeyStore, create an instance of webhooks.Helper using functions in our webhooks package:
helper, _ := webhooks.V1().NewHelper(store)Use the webhooks helper
From an entrypoint that you should write yourself, call the Unmarshal method of the webhooks.Helper object. It takes the following arguments:
- The body, as a string. This should be the raw body as received from the webhooks system.
- A list of request headers as received from the webhooks system.
If the body is modified, even in the slightest way like replacing line breaks or adding a trailing line break, signature validation will fail.
In code:
event, _ := helper.Unmarshal(body, requestHeaders)Notes
Error handling
Many of the code snippets presented on this page ignore errors returned by function or method calls for simplicity. When using the SDK in production, make sure that all errors are properly handled.
Renaming of properties
The Go SDK uses Go naming conventions as much as possible. The first letter of each property is turned into upper case, and several acronyms in properties have been turned into upper case. For example, hostedCheckoutSpecificInput is called HostedCheckoutSpecificInput, and paymentId is called PaymentID.